-

Evaluating the Effects of Contraceptive Use on Breast Pathology and Tissue Density Using Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
Madison Fleischman
This poster discusses how the long-term use of hormonal contraceptives can affect breast density and pathology, and the efficiency of 3-Dimensional (3D) mammography in evaluating dense breast tissue and detecting these pathologies. The results of research on long term use of estrogen-based hormonal birth control and its effect on breast tissue density and the risk of breast cancer, the relationship between breast tissue density and risk of breast cancer, and the efficiency of 3D vs. 2-dimensional (2D) mammography in screening dense breast tissue and identifying breast pathology are presented. Results of the studies show that long-term exposure to hormonal contraceptives and breast tissue density are directly related to the risk of breast cancer. They also support 3D mammography as more efficient and accurate than 2D mammography in evaluating dense breast tissue and identifying breast pathology in dense breasts. The poster emphasizes the importance of annual mammography screening to detect any changes in the breasts, as well as the need for 3D mammography to provide more accurate and efficient imaging of women with dense breasts and those using hormonal contraceptives.
-

The Effectiveness of Exercise in the Prevention of Gestational Diabetes: A Systematic Review
Gabrielle Freed SPT, Amanda Sheehan SPT, Amy Sokol SPT, and Haley Stack SPT
Background: Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy and can cause complications for the mother and baby. Poor management of gestational diabetes can lead to a large sized baby, Cesarean section at delivery, preeclampsia, or hypoglycemia in the baby at birth. Physicians advise women, pre-conception and post-conception, to follow a diet and exercise plan in order to decrease the chances of developing gestational diabetes. Studies have been done to determine the effectiveness of proper diet and exercise prior to conception and during pregnancy in the prevention of gestational diabetes.
Purpose: The purpose of the review was to evaluate the role of exercise in preventing gestational diabetes and maternal weight gain.
Methods: A literature search using four search terms (gestational diabetes, exercise, pregnancy, and weight gain) and three filters was performed utilizing PubMed. A screening process and a hand search were done to create a list of twelve articles to be included in the systematic review. Articles were analyzed for quality using a hierarchy of evidence scale.
Results: Twelve studies met the inclusion criteria. All were classified as 1b or 2b level of evidence.
Conclusion: The chosen studies provide evidence that support the idea that risk for gestational diabetes can be decreased through weight management and exercise before and during pregnancy. Exercise during the pre-conception period and the first trimester has been found to help reduce the risk of gestational diabetes. Further research is needed to determine the most effective form of exercise.
Implications: Physical therapy prior to and during pregnancy should be prescribed by physicians in order to help prevent the onset of gestational diabetes. Physical therapists specialize in developing exercise programs, educating patients on nutrition and wellness, and preventing injury due to pregnancy related physical changes.
-

Effectiveness of physical therapy interventions in the treatment of urinary incontinence in older women: a systematic review
Ariana Gagliardi, Lauren Paretti, Kayla Stephani, and Stephanie Oliverio
Background: Urinary incontinence (UI) is a prevalent condition among older adults. While age and gender are risk factors, UI is not a natural part of female aging. By not seeking proper care, these individuals may be hindering their independence, opportunities to receive effective treatment, and their overall quality of life. Research shows a wide variety of physical therapy (PT) treatment options are available for UI.
Purpose: The purpose of this systematic review was to examine the effectiveness of various conservative PT interventions in treating stress, urge, and mixed UI in older women.
Methods: Two searches of the literature were performed in September 2019 and February 2020. All articles were analyzed for quality on the PEDro scale and a hierarchy of evidence scale. Studies that examined stress, urge, and mixed UI were evaluated.
Results: Sixteen articles were included in the results. Dependent variables included instruments, such as questionnaires, scales, and/or bladder diaries, that measured outcomes of UI symptoms.
Conclusion: Studies examining PT interventions for the management of UI generally found that pelvic floor muscle training, electrical stimulation, behavioral therapy, extracorporeal magnetic innervation, and physical activities were effective in reducing UI symptoms.
Implications: PT interventions have been shown to be effective in the management of UI and should be the first line of treatment as opposed to non-conservative methods. Physical therapists can and should apply this knowledge in their practice when treating UI in older women. Physicians should consider referring to PT prior to prescription of medication or referral to surgery.
-
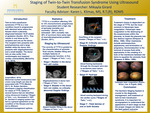
Staging of Twin-To-Twin Transfusion Syndrome Using Ultrasound
Mikayla Catherine Girard
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a rare condition found in identical twins in which the fetuses share a placenta. It is diagnosed between 16-24 weeks of gestation using ultrasound imaging and the Quintero staging system. The Quintero staging system includes 5 stages, which are categorized by sonographic findings to include abnormal Doppler findings, amount of amniotic fluid, as well as determining which twin is the recipient and which is the donor. The last stage determines if fetal demise in one or both twins has occurred. Dr. Quintero’s staging system has led to an agreement on the condition of the fetuses, as well as the development of treatment and/or management options that are available at each stage. Treatment options include fetoscopic laser coagulation and amnioreduction. TTTS affects 10-15% of monochorionic pregnancies and has a greater than 90% mortality rate when left untreated.
-

Does IPE Improve Patient Safety?
Wendy Guzenski
Interprofessional Education improves patient safety through collaboration and the common understand of patient care decisions and goals.
-

Bootstrap: Simulating the Cure
Heather Harvey
The final project in STA 486, is to create a poster on an analysis done on a real life data set. This poster is describing a simulated bootstrap done on a data set about the band The Cure. It shows a 95% confidence interval on the effect that a songs danceability, liveness, and energy have on its popularity.
-

Internship with Alison's Homemade Welsh Cookies
Heather Harvey
During the Spring 2020 semester, I have been undergoing an internship with Alison's Homemade Welsh Cookies. They have allowed me full access to their data, in order to perform an analysis. Using the sames records from the 2019 year, each location has been identified on a map and the amounts sold tell which ares had the most and the least sales in 2019.
-

Nurse Residency Programs, A Solution to the Nursing Shortage
Kylie Hibbett
The nursing shortage has become an increasing problem for the healthcare field with statistics estimating the problem is only going to worsen as the years pass. New graduate nurses compromise a small percentage of the nursing workforce, but can help lessen the burden of the shortage. Nurse residency programs have been shown to increase the retention of new graduate nurses. By implementing nurse residency programs, there can be a viable solution to decreasing the nursing shortage that is currently affecting patient outcomes and care.
-
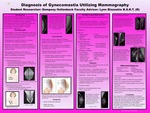
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia Utilizing Mammography
Dempsey Hollenbeck
Mammography is a low dose radiographic imaging of the breast tissue. Screening and diagnostic mammography are both utilized to examine breast tissue, however diagnostic mammography is only performed on patients presenting with symptoms. Gynecomastia is a benign enlargement of male breast tissue that may occur at any age. Gynecomastia is often idiopathic, but there are multiple possible causes involving hormones, conditions, medications, and substances. Gynecomastia presents radiographically different depending on how long it has been present in the body. The different diagnosis patterns are early dendritic, late dendritic, and diffuse glandular. Many pathologies in the male breast present similarly on a radiograph. Some differential diagnoses include male breast cancer, Pseudogynecomastia, and lipoma. The aim of this research is to evaluate the diagnosis of gynecomastia utilizing mammography. Many aspects of gynecomastia are examined, including symptoms, possible causes or risk factors, diagnosis, diagnosis patterns, and differential diagnosis. Future work may involve research on the specific causes of gynecomastia in the older population and treatment options for gynecomastia.
Keywords: Mammography, Gynecomastia, Diagnostic Mammography, Male Mammography
-

Are Healthcare Workers in the Hospital Ready for Disasters in the Community?
Nicholas Hromek
This poster presents the idea that healthcare workers in hospitals are not equipped for disasters in the community. During such a vulnerable and relevant time such as the COVID-19 pandemic, this poster focuses on the pitfalls of the healthcare and hospital system.
-

Uninsured/Underinsured: Who's Problem Is It?
Manpreet Kaur
The problem of uninsured and underinsured in terms of health care was implored in the population of the United States of America. Other developed nations have implemented universal health care whereas the United States have fallen behind. It is an ongoing problem in the nation, and it is not only the problem of the people who face being uninsured and underinsured. It is everyone’s problem because it affects the economy as a whole and every person is affected by the way the country decides to treat health care. Nurses, as health care professionals, have the opportunity to help patients access health care and provide other resources that may be beneficial.
-

Crowded ER Waiting Rooms – Are Freestanding ERs the Way To Go?
Jesse Keats
This poster discusses the differences in freestanding and hospital emergency departments. My position on this topic focuses on the idea that free standing ERs do not reduce overcrowding in an emergency room.
-

The Effects of Rolipram, a Selective Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor, on Immortalized Schwann Cell Proliferation
Kyle Kenney, Amanda Bohn, and Angela Asirvatham
The regulation of Schwann cell growth in vitro is facilitated by heregulin, a neuron-secreted growth factor, and an unknown mitogen that activates the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) pathway. The quantity of cAMP available to Schwann cells can determine if they become a myelinating or proliferating phenotype. The abundance of intracellular cAMP available to the cell is widely regulated by a family of enzymes called phosphodiesterases (PDEs). PDE inhibitors such as rolipram have therapeutic potential in various disorders and function by increasing the levels of cAMP in the cell. This study was undertaken to determine the concentration of rolipram that would induce optimal Schwann cell proliferation. It was hypothesized that an increase in rolipram levels will elicit a dose-dependent rise in cell proliferation.
-

QI: Saving Skin, Saving Lives
Carrie Ann Kinney
Quality Improvement (QI) projects are interprofessional team efforts, developed to improve health-care quality. Pressure injury prevention has been identified by the National Database of Nursing Quality Indicators (NDNQI) as a key nursing sensitive outcome. QI projects such as the Deal with Heels project, the Save Our Skin program, and the implementation of designated turn teams have significantly reduced the incidence of hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs). This has reduced the risk of patients developing severe complications, which significantly improves health outcomes.
-

The Effects of Medical Cannabis and Physical Therapy in Patients with Chronic Pain and/or Parkinson's Disease: Protocol Study
Jake Kocovsky SPT; James Pedersen SPT; Brandon Winslow SPT; and Maureen Pascal PT, DPT, NCS
Background. There is limited research exploring how physical therapy coupled with medical cannabis use in patients with chronic pain and/or Parkinson’s disease can improve function and affect life satisfaction among patients.
Objectives. The purpose of this study is to determine the effects of medical cannabis coupled with skilled physical therapy in patients with Parkinson's disease and/or chronic pain.
Design. This would be a randomized experimental study containing 4 separate subject groups: medical cannabis and chronic pain, no cannabis and chronic pain, medical cannabis and Parkinson’s disease, no cannabis and Parkinson’s disease.
Setting. Misericordia University Pro Bono Clinic, Dallas, PA
Participants. Researchers would recruit a total of 80 subjects, 40 with chronic pain and 40 with Parkinson’s disease. All participants would have a legal prescription for medical cannabis in the state of Pennsylvania.
Intervention. PT interventions may include, but are not limited to: exercises to work on balance, strength or flexibility, mobility training and manual therapy. Interventions would vary based on the subjects’ needs and presentation.
Measurements. The outcomes measures used in this study would be The Numeric Pain Rating scale, Life Satisfaction Questionnaire-11, postural assessment using the Posture Screen Mobile application, and the gait parameters measured on the Zeno electronic walkway.
Limitations. Perceived safety of subjects, small sample size, lack of current research in this realm.
Conclusion. Researchers believe this research to be vital and important to the realms of physical therapy, medical cannabis, chronic pain and Parkinson’s disease and hope it can be carried out by future researchers.
-

Nurse Migration and the Effect on Source Country
Taylor Lane
Even though there are some positive effects on source country of nurse migration, nurse migration has led to a severe shortage of nurses in source country which has led to decreased health and wellness in the source country.
-

The Effects of Rhythmic Exercise on Reaction Time and Balance in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Protocol for a Single-Session, Pretest/Posttest Study
Joseph Levandowski, Anthony D'Eliseo, Jacob Klein, and Damian Pierontoni
Dancing, both as a therapeutic technique and a recreational hobby, has been widely implemented as an exercise modality in order to improve both functional and metabolic outcomes, and its concepts have been applied to the older adult population (65+). The act of dancing encompasses various rhythmic and repetitive motions within functional movement patterns that can have a direct impact on balance, endurance performance, functional outcome measures, and reducing the incidence of falls within this population. A majority of dance programs and research studies concerning dance techniques have been centered at viewing its effects and outcomes that occur following an extended timeframe, including interventions lasting weeks to months. This pilot study is designed to perform rhythmic movements in the form of dance and assess their ability to influence UE and LE reaction times and balance following a single intervention session within an older adult population. The information gathered from this study will add to the literature about rhythmic movements and their impact related to interventions that may be utilized to prevent falls within the older adult population.
-

Why Uninsured Americans Burden The Health Care System
Lindsay Mckim
This poster exemplifies the burden that is put on the health care system specifically emergency rooms when Americans are unable to afford health insurance. It highlights the importance of health insurance and how critical it is to be able to attain health insurance for all. The lack of health insurance is being seen in these emergency departments creating longer wait times and poorer quality care because that is the only place people without insurance can get care, thus creating a burden on the health care system.
-

Core Measures Work...As Long As We Put in the Time
Miranda Moser
Heart Failure is a serious problem in the United States that affects millions each year. Core measures were created for hospitals as a standard of care for specific diseases. This research poster focused on Heart Failure core measure 1: discharging teaching that must be provided to a patient that encompasses six key areas related to heart failure management. Statistics and various studies were drawn from and analyzed to support the position of this poster, that these discharge teachings, when conducted properly, significantly reduce the rate of hospital readmissions of heart failure patients.
Student Research Poster Presentations showcase innovative research by Misericordia students across all disciplines.
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.







