Student Research Poster Presentations showcase innovative research by Misericordia students across all disciplines.
-

Reducing Dose In Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA)
Mariah Ambrosio
This project describes the different techniques that can be implemented during coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) to reduce patient dose. CCTA exams are becoming increasingly popular in diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD) due to its noninvasive nature. However, CCTA exams provide some of the greatest radiation dose of any computed tomography exam. As a result of this exam, patients can receive a total effective dose anywhere from 15 millisieverts (mSv) to 20 mSv and higher. This project discusses reducing dose by means of electrocardiogram (ECG) – triggered prospective gating, reducing tube potential and bolus tracking. Also, the proper use and limitations of these techniques are specified to ensure proper use each dose reduction method. These limitations include a resting heart rate between 50-65 beats per minute (BPM) and a body mass index (BMI) of < 30 kg/m2. The correct use and implementation of these techniques can result in an average 31% to 72% total reduction of patient dose without compromising image quality.
-

The United States Should Have a Universal Healthcare System
Ian Anderson
The U.S should opt-in for universal health care. Lack of healthcare results in poorer health for individuals, communities, and the entire nation by limiting opportunity, health, and the ability to live with dignity and freedom.
-
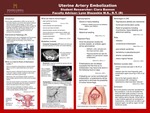
Uterine Artery Embolization
Ciara Bannon
Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE) is a procedure commonly used to treat post-partum obstetric hemorrhaging. Interventional Radiology is the department that utilizes the procedure in conjunction with labor and delivery as well as the nursing staff and physicians. This procedure can also be used to treat uterine fibroids, scar tissue formations, and adenomyosis. There are multiple embolization agents that can be used including coils, Gelfoam, glue, or a combination of all three. There are risks that are associated with this procedure and it is not always successful the first time it is completed. High success rates were seen in many case studies, ranging from 95%- 97%. If complete failure is experienced, the patient would undergo a hysterectomy to control the bleeding and in some rare cases, death has resulted. After research was conducted it can be concluded that Uterine Artery Embolization is a highly successful procedure to be executed and can even leave patients with the ability to become pregnant again afterwards and maintain their normal menstrual cycle.
-

The Effect of Different Balance Training Protocols on Athletes with Chronic Ankle Instability: A Systematic Review
Jonathan Boruta, Nate MacDonald, Zackery Wroniuk-Evans, and Joshua Wilkes
Chronic Ankle Instability (CAI) is a prevalent topic in the world of sports physical therapy due to the high incidence of ankle sprains among athletes. Differing opinions on methods of treatment for CAI has generated an influx of research regarding the effectiveness of different treatment protocols. Unstable balance training, plyometrics/hop stabilization training, resistance training with balance, and combined interventions are currently being researched to determine their effects on athletes with CAI.
-

The Efficacy of Using Blood Flow Restriction Training on Proximal Muscle and Joint Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review
Bailey Brugler, Tristan Wright, Evan Brown, Johnathan Warg, and Matt Cuomo
Background: Blood flow restriction training (BFRT) when used with low-load exercise can improve muscular strength and recovery time in individuals attending rehab for distal extremity pathology. Current research suggests that BFRT when used proximally may elicit similar results.
Purpose: The aim of this systematic review was to analyze evidence regarding the efficacy for physical therapists to utilize BFRT for individuals attending therapy for proximal joint or trunk related injuries.
Method(s): A literature review was conducted by five reviewers using CINAHL, Medline, EBSCO, and Academic Search Ultimate. Articles were examined using the search terms (BFR or Blood flow restriction or Blood flow restriction training) and (trunk or hip or shoulder or proximal). Exclusion criteria consisted of the following: PEDRO Score < 3, publication date prior to 2010, systematic reviews or meta-analysis, and if the articles were not peer reviewed.
Results: Of the 253 results produced in the search, 11were selected and considered to be eligible. Articles were examined using the PEDro Scale and Hierarchy of Evidence Scale from the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. The 11 articles were then grouped into one of the following categories: BFR and the proximal UE, BFR and the proximal LE, BFR and the Trunk, or BFR and systemic effects of the UE, Trunk, or LE. Upon further evaluation we determined that BFRT when used proximally produced the following improvements: increased CSA/strength, tendon thickness, Hb transport, increased perfusion, functional capabilities, balance, endurance, and decreased pain, and positive responses to metabolic stress.
Conclusions: When used in healthy and already active populations, BFRT is a safe and effective compliment when used with exercise. Further research is required in order to determine the efficacy of using BFRT in individuals who are potential candidates for physical therapy rehabilitation. We recommend research be conducted while implementing a standardized BFR protocol in order to more consistently produce results that might further determine the efficacy of using BFRT on the proximal UE/LE and trunk for the purpose of joint/muscle rehabilitation.
-
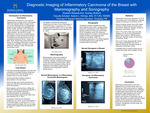
Diagnostic Imaging of Inflammatory Carcinoma of the Breast with Mammography and Sonography
Aubrey Bullock
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma (IBC) is a rare type of breast cancer with a high incidence of metastases that makes the breast tender, red, swollen, and sometimes exhibits an orange peel appearance. These type of cancer cells block lymph vessels in the skin of the breast and develops rapidly. Risks factors include sex, lifestyle, age, reproductive factors, race, obesity, and family history. Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer deaths among women. Approximately 1 in 8 women have a risk of developing breast cancer. The most accurate way to diagnose inflammatory breast carcinoma is via mammography and/or sonography. Mammography/and or sonography have the ability to delineate benign versus malignant disease processes, as well as location and types of breast cancer. They can both aid in early detection and prevention, pointing to an increase in five year survival rate. Mammography and/or sonography serve as the primary identification point to guide the need for further analysis and treatment to improve the patients overall quality of life.
-

Nurses Can Make A Difference on the Impact the Uninsured/Underinsured Have on Health Care
Robert Burke
The uninsured rate has increased from 2016 to 2019 and due to the Covid-19 outbreak in 2020 and unemployment, that number has likely jumped. Health care has proven to be costly, and the uninsured/underinsured population is viewed as a vulnerable population in the community due to a financial barrier or unemployed status that hinders their ability to receive the health care they need. It is proven that the uninsured/underinsured are more likely to forgo preventative care due to financial reasons. In addition, because the uninsured/underinsured are more likely to forgo preventative care they are more likely to be hospitalized with avoidable conditions and also do not receive the services or care for major health conditions and chronic diseases. Prevention is cheaper than maintenance of chronic conditions. Maintenance of chronic conditions may require additional resources that prove to be costly for the individual and the health care systems. Therefore the uninsured/underinsured impact the health care system by being more likely to be admitted for an avoidable condition and proving to be costly to the health care system. Nurses can help the uninsured/underinsured to improve their health and receive the care they need by being the patient’s greatest advocate and referring them to appropriate resources. Nurses can refer patients to free clinics. Being the patients’ greatest advocate and referring them to appropriate resources can help improve the uninsured/underinsured patients’ health status, which would ultimately reduce costs and improve the patients’ quality of life.
-

The Impacts of Health Insurance on the Uninsured and Underinsured
Isabela Camayd
In the United States the American healthcare is constantly up for debate, it seems to only be aimed towards individuals who can afford insurance. Those individuals who can afford insurance must have a full-time or part time job to obtain the benefits from the employer. For those individuals who are underinsured and uninsured there could be endless reasons holding them from obtaining their own insurance, private insurance, company insurance and many others. There are a few organizations in place to help those who are in need of insurance such as, the Affordable Care Act, Medicare and, Medicaid.
-

The Effects of Resistance Exercise Training on Quality of Life and Muscle Strength in Patients Undergoing Cancer Treatment: A Systematic Review
Rachel A. Carmody, Evelyn S. Logie, Hannah J. Larkin, Kaitlyn E. Yurenda, and Zachary M. Mason
BACKGROUND: Breast cancer and prostate cancer are two of the most common cancers seen in females and males respectively worldwide. Treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, and androgen deprivation therapy are essential to combat cancerous cells. However, the lasting side effects of these lifesaving treatments can impact an individual’s quality of life and muscle strength without appropriate intervention. While exercise has been shown to be beneficial for patients with cancer, there is limited understanding of the effects of resistance training when performed concurrently with medical interventions.
PURPOSE: The purpose of this systematic review was to evaluate the impact of resistance training on quality of life and muscle strength in patients with breast and prostate cancer undergoing cancer treatment.
METHODS: An academic search was conducted beginning August of 2020 and ending January 2021. The databases searched consisted of PubMed, EBSCO, Academic Search Ultimate, CINAHL, and Medline. This search yielded 18 randomized controlled trials, 11 pertaining to breast cancer and 7 pertaining to prostate cancer.
RESULTS: All articles utilized a myriad of outcome measures to see changes in QoL and muscle strength. Studies evaluated resulted in either a positive short term or no improvement during the period of active intervention. However, some studies did note a lack of long-term significant differences in outcome measures between the intervention and control groups. Review of the literature did not reveal patient attrition was due to adverse effects of the intervention.
CONCLUSION: Resistance training can be a safe and effective intervention to improve quality and life and muscle strength in patients undergoing cancer treatment. Current studies demonstrate the need for physical therapists to be included in the interdisciplinary approach from the moment of a cancer diagnosis.
-

Anti-Semitism in France: How the Post-Holocaust Era Informs French Attitudes Today
Alyssa Chesek
Following the end of the Holocaust, approximately 160,000 native Jews and 20,000 displaced Jews arrived in France. France, which operated under the Vichy government during World War II, was a Nazi puppet regime complicit in the persecution of its Jewish population. When Vichy fell in 1944, the recently instated Provisional Government of the French Republic became responsible for Jewish restitution and reintegration services. However, the new government refused to recognize a Jewish problem; this denial resulted in inadequate services and protections for the Jewish population. Without providing Jews with proper legal protections, the French government created an environment which may have contributed to the persistent anti-Semitism that has plagued the nation since the 1940s.
-

Nursing Migration and its Impact on Source Countries
Noah Joao Dean
Developed countries have been recruiting international nurses at an increasing rate. Nursing migration has become an ethical issue in our world as it increases the disparities that separate developed countries and developing countries.
-

Without EBP, Where Would The Nursing Profession Be Today?
Robin Erb
Evidence based practice (EBP) is used in nursing to better deliver care to patients throughout the entire United States.
-

The Positive Effects of Malpractice in Nursing Practice
Jennifer Evans
Malpractice to some has been viewed as a negative topic in nursing practice. However, it actually allows for positive influences to effect nursing practice. With the ongoing threat of lawsuits, it allows nurses to be better educated and learn from what not to do in their practice. It allows supervisors, and any other healthcare team member, to become more involved in the practice. Overall, it allows for the continuance of the safest care possible to patients.
-

Efficacy of Using Virtual Reality Systems to Enhance Balance in Individuals With Vestibular Disorders: A Systematic Review
Alexander Fitch, Leanne Forsyth, Jennifer Freeman, and Kailey Vogl
Background: A common impairment with vestibular disorders is diminished balance. Previous systematic reviews have analyzed the efficacy of virtual reality (VR) systems in vestibular rehabilitation in both clinical and home settings. However, none have specifically focused on the improvement of balance with VR systems in individuals with peripheral vestibular disorders.
Purpose: The purpose of this systematic review was to assess the efficacy of using VR systems to treat balance impairments in individuals with peripheral vestibular disorders.
Methods: Two searches were completed, the first in August 2020 and the second in January 2021. Databases searched included: EBSCOhost (CINAHL Complete and Medline) and PubMed. Search terms for the EBSCOhost databases included: ‘virtual reality OR vr OR augmented reality’ AND ‘vestibular rehabilitation OR vestibular therapy’. For PubMed, the search terms were ‘virtual reality AND vestibular disorders’ and ‘virtual reality AND balance’. A single hand search was also utilized.
Results: Ten articles were included for analysis. This systematic review determined that virtual reality systems are an effective way to improve balance in individuals with peripheral vestibular disorders. Previous literature was also supported in that it is best to combine VR rehabilitation with conventional vestibular rehabilitation exercises for the most effective treatment of individuals with peripheral vestibular disorders.
Conclusions: Future research should focus on standardizing an outcome measure to best assess balance changes in individuals with peripheral vestibular disorders as a result of using VR-based treatments. This would also allow for further analysis of the effectiveness of different types of VR systems in vestibular rehabilitation.
-

The Importance of the Time’s Political Climate in Cases of Incitement
Kimberly George
The Supreme Court cases, Schenck v. United States (1919), Dennis v. United States (1951),and Brandenburg v. Ohio (1969) each deal with the issue of incitement speech. Each create tests for determining what is incitement speech which is not protected under the First Amendment. Each of these cases took place during times with tense political climates, World War One, the Cold War, and the Civil Rights Movement. This had an impact on the outcomes of these cases.
-
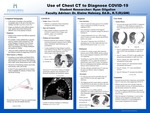
Use of Chest CT to Diagnose COVID-19
Ryan Gilgallon
Use of Computed Tomography (CT) to Diagnose COVID-19
Ryan Gilgallon
Dr. Elaine Halesey, Ed.D., R.T.(R)(QM)
This project explains COVID-19 and the role Computed Tomography (CT) can play in diagnosing patients who have infections. General equipment used, symptoms, findings and abnormalities, methods of early detection, rates of misdiagnosis, advantages of CT, and a case study are also discussed. COVID-19 originated in Wuhan, China and rapidly spread throughout the world being transmitted from human to human, affecting the respiratory system. The most common findings in this project consisted of ground-glass opacities (GGO), fibrous stripes, interlobular septal thickening, and consolidation. Computed Tomography is a non-invasive procedure which is effectively used to detect, treat, manage, and track recovery of patients infected. With a low misdiagnosis rate of 3.8% and early detection of 2.61 days compared to RT-PCR test result, it proves that CT is an accurate tool to diagnose COVID-19. As technology advances, infections such as COVID-19 can be managed and treated through the use of Computed Tomography.
-
Magnetic Resonance Neuroblate Fusion for Treating Glioblastomas
Amanda Goldy
The Neuroblate Fusion system utilizes magnetic resonance guided laser therapy to ablate tumors and lesions. The system requires the use of Laser Interstitial Thermo Therapy (LITT) to activate thermocoagulation and focus of tissue destruction. This is a minimally invasive alternative to traditional brain surgery, giving patients a shorter recovery time and fewer complications. Neuroblate Fusion may also be an additional treatment to chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Neuroblate Fusion is best used for treating glioblastomas in the brain and occasionally for reducing the potential for seizures. Under sterile conditions, a small burr hole is made in the patient’s skull which allows the neurosurgeon to accurately place the probe onto the area of interest. Concurrently with the neurological procedure, real-time magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is performed. This helps to assist the surgeons in precisely locating the glioblastoma and destroy the carcinogenic tissues with the laser, while avoiding the surrounding healthy tissues and anatomy. Neuroblate Fusion is a great treatment option for patients who are suffering with aggressive tumors such as glioblastomas. Laser therapy gives patients a new hope and a better chance of survival. Recurrence of glioblastomas are common after patients undergo a first surgery without the use of Neuroblate Fusion. Destroying the tumor proves to be more successful after a second surgery is done using laser therapy. In the future, Neuroblate Fusion may become the gold standard for treating glioblastomas.
-

Money Makes The World Go Around
Madisyn Granoski
The United Nations set forth 17 sustainable goals aimed at changing out world for the better. Goal 1 is No Poverty. This poster shows the significance of poverty along with ways we can end poverty, and advocate for those less fortunate.
-

Protocol: The Effectiveness of Telehealth as a Means for Administering Physical Therapy
Haley Gruber, Samantha Missal, and Gerald Vitale
Background: The Coronavirus pandemic has led more researchers to study the effectiveness of telehealth as a means for administering healthcare services. Prior to the pandemic, there has been limited research regarding the use of telehealth within the healthcare industry. More research relating to telehealth has been conducted within the past two years due to its growing relevance relating to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Objective: The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of telehealth as a means for administering physical therapy services.
Design: This will be a descriptive analysis research study design carried out through the means of an electronic survey. A paper or electronic flyer for this study provides a QR code and direct URL link for participants to access the electronic survey.
Setting: The participants will be obtained through Pro Bono clinics that are willing to participate in the study who are registered in the Pro Bono Network. Analysis will be performed at Misericordia University in Dallas, Pennsylvania.
Participants: We hope to obtain 100 participants to complete our survey. The participants will include patients/caregivers, physical therapists, student physical therapists, physical therapist assistants, and student physical therapist assistants who have participated in telehealth physical therapy sessions.
Data Analysis: Descriptive statistics
Limitations: Limitations include that a small number of patient visits via telehealth may influence their opinion on their telehealth experience. There is a limited sample size of participants to complete the survey. Population is specific to pro bono clinics within the pro bono network. Survey research only provides data collected from a single point in time and is therefore difficult to measure changes in the population.
Conclusion: Preliminary interviews with patients/caregivers and therapists outside our targeted population, along with available research suggests that the use of telehealth as a means for administering physical therapy is an effective, but limited method to deliver services.
-

Effectiveness of Physical Therapy Interventions for Women with Dysmenorrhea: a Systematic Review
Emily Hammond, Abigail Applegate, Emma Caldwell, Hayley Witmer, and Amy Tremback-Ball
Background and aims: Primary dysmenorrhea, or painful menstruation, is common in menstruating females. However, in some, it can cause intense pain, disrupt activities of daily living, and impact quality of life. The treatment of dysmenorrhea does not traditionally include physical therapy. A systematic review was conducted to explore the role of physical therapy in treating dysmenorrhea. Methods: A search was performed in August 2020 and January 2021 using EBSCOhost, Academic Search Ultimate, CINAHL Complete, and MEDLINE. Search terms included exercise or physical activity or fitness AND dysmenorrhea or menstrual pain or painful menstruation. Inclusion criteria were articles that were peer-reviewed, published in the last 10 years, and available in full text in English. All articles included in the review were analyzed for quality on a hierarchy of evidence scale.
Results: 22 results were included in this systematic review. 19 articles were level 2 and 3 articles were level 3 on the hierarchy of evidence scale. The Visual Analog Scale and Menstrual Distress Questionnaire were the widely utilized outcome measures used to determine the effectiveness of the interventions. Interventions including aerobic exercise, stretching, kinesio taping, aquatic therapy, acupressure, yoga, core stability, positional activities, spinal manipulation, and patient education have shown to be effective.
Conclusions: Physical therapy can assist in the reduction of pain and other symptoms associated with dysmenorrhea. Overall, articles indicated that aerobic exercise, stretching, and core stability yielded the greatest improvement in patient symptoms of dysmenorrhea. Physicians should consider recommending physical therapy to patients with symptoms that disrupt their activities of daily living.