Student Research Poster Presentations showcase innovative research by Misericordia students across all disciplines.
-
Do Core Measures Improve Patient Outcomes in MI, Pneumonia, and CHF?
John Merrifield
Implementation of core measures developed by the Joint Commission improves health outcomes in patients with Acute Myocardial infarction (AMI), Congestive Heart failure (CHF), and Pneumonia. In addition, these core measures can decrease hospitalization costs and these savings are passed onto patients with lower hospital bills at discharge.
-

Treatment of Orbital Lesions using CyberKnife Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Emily Morahan
The purpose of the research done was to evaluate the use of CyberKnife Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) for treating orbital lesions. Efficacy and tolerability of such treatment was analyzed with data drawn from multiple sources, regarding dose and fractionation, quality of life following treatment(s) and prognosis. CyberKnife SRS is the newest, most advanced model of radiation delivery systems, featuring a robotic arm capable of manipulating the linear accelerator into thousands of unique angles. The addition of new angles allows for a more precise concentration of radiation delivered to the lesions. In the case of optic lesions, it is crucial to minimize dose to adjacent structures such as optic nerve, lens and fovea. CyberKnife SRS is superior for treatment in small anatomical locations due to steep dose gradients and target localization system, allowing maximum sparing of organs at risk. While CyberKnife SRS is rapidly becoming the gold standard for orbital lesions, there is still a likelihood that other treatments may be required as an adjunct therapy for treatment purposes. However, current research identifies the high success rate of CyberKnife SRS but acknowledges the need for further research in dosage and fractionation.
Keywords: CyberKnife, Orbital Lesion, Radiation therapy, Cancer treatment
-

Atomic Anxiety and the Interstate
Andrew Oidtman
The National Interstate and Defense Highways Act of 1956 was a much needed piece of legislation that provided the nation an integrated interstate system while also quelling the atomic anxiety that was rampant during the early years of the atomic age. Atomic and communist anxiety was the lynchpin that allowed for interstate legislation to garner support from the American people and federal government. The connection between the interstate system and civilian defense first adopted by President Eisenhower in 1955 as a serious matter accomplished two important tasks. It allowed for the American people to accept increased taxes and allowed the federal government to increase funding based on national security. The unintended consequences of the National Interstate and Civilian Defense Act of 1956 were many. Most notably, the American people's relationship with the open road was forever altered. Leisurely backroad drives which defined open road culture were replaced by the tedium of interstate driving as the road became incorporate with the gray flannel suit of corporate America.
-

Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva -Second Skeleton
Emily Paciga
For my poster presentation, I chose how disease, illness, and sickness are defined differently in medicine. Specifically, the humanities bring awareness to treating the person as a whole rather than their prognosis. The ability to differentiate the aforementioned criteria allows for the individual to have the best treatment and outcome. I decided to show how within Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP) there are different definitions of the diagnosis.
The poster delves into the definition of disease as the medical definition of the diagnosis—essentially, what the doctor informs to the patient. With FOP, common characteristic of the disease include stiff rigidity of the shoulders and neck, the inability to walk, and randomized flare-ups that cause painful calcified growths muscles and tissues that surrounds the skeleton.
Illness is how the individual experiences their own prognosis. Jasmin Floyd is an activist who, through social media, has brought awareness to FOP and how she has learned to live with the terminal diagnosis.
Sickness is how society has stigmatized the diagnosis. Flare-ups due to FOP cause people to look different than others. Creating a hurdle that may not have been addressed in the disease diagnosis as something an individual has to think of. How will society view me? Comments like mannequin and statue are a few examples of the negative connotations used.
To conclude, the humanities in health care bring awareness to treating the person as a whole rather than their prognosis. Having the ability to differentiate the aforementioned criteria allows for the individual to have the best treatment and outcome.
skeleton, FOP, disease, illness, sickness
-
Implementation of Intravascular Ultrasound for Percutaneous Coronary Interventions
Emily Pellam
This poster demonstrates how intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) plays a role in the diagnosis and treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD). A percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a commonly performed and minimally invasive treatment that is often enhanced by the use of IVUS. Catheters are inserted into peripheral arteries and revascularization of the coronary arteries is completed with the use of angioplasty balloons and stents. IVUS is used before an intervention to diagnose and measure stenotic lesions and used after to assess stent expansion and possible complications. Definitions, indications, and contraindications are included for IVUS and PCIs as well as general discussion of outcomes. Included research shows better patient outcomes for PCIs completed with IVUS than with angiographic guidance alone. IVUS is shown to increase the length and diameter of stents and postdilation balloons used during a PCI. Research also shows that ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients have better outcomes with IVUS use. Overall, patients have better outcomes after PCI with the enhancement of IVUS. The limited use of IVUS indicates the need for more extensive research and increased rates of implementation.
-
COVID-19 in the Computed Tomography (CT) Department
Jannelle Perla
This research will discuss how Coronavirus (COVID-19) has severely impacted the world and the role of computed tomography (CT) department as a whole. COVID-19 is an infectious disease that is fast spreading caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The outbreak began in December of 2019 in the city of Wuhan, China. COVID-19 has been declared a pandemic since March of 2020 due to the rapid spreading of the virus. The most common way to confirm coronavirus is the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) nasal swab. X-ray and CT are the two main imaging modalities that help rule out, detect, and are used to observe progression of the virus within the patient’s body. The virus mainly impacts the lungs of patients who show severe symptoms. The different pathologies commonly found in patients with COVID-19 will be explored. The appearance of ground glass opacities (GGO) is seen on chest CT scans as a common pathology in patients with COVID-19. The virus has impacted the world as a whole, but research and development of the COVID-19 vaccine have become available. The COVID-19 vaccine will help to prevent people from contracting the virus.
-

Sonography Education in Australia, Canada, and The United States
Sierra Pettit and Haley Bechdel
Sonographers are healthcare professionals who perform medical diagnostic procedures that use high frequency sound waves to produce visual images of human organs, tissues, or blood flow inside the body. Sonography students must attend either secondary degree programs or postsecondary degree programs, depending on the country in which they receive their education. In this Literature Review, a comparison of the secondary and post-secondary educational process within Australia, Canada, and the United States will be discussed. An overview of the general primary and secondary educational systems are briefly described. The different accrediting and credentialing bodies are discussed in each of the three countries. Australian sonography program accreditation is performed through the Australian Sonographer Accreditation Registry (ASAR). The programmatic accrediting body in Canada for sonography programs is known as the EQualTM Accreditation. The sonography programs in the United States receive accreditation through the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP). Understanding the various educational systems, as well as the accrediting and credentialing bodies in Australia, Canada, and the United States allows those interested in working in these countries to gain knowledge in the pathway to become a sonographer.
-

Analysis of Methods to Measure Heart Rate in Mytilus edulis
Kristin Pinho
Non-invasive research will be performed to limit the additional stress from equipment and focus on the harmful effects that polluted run-off water has on mussels’ heart rates. The chemical that will be introduced to the laboratory environment will be weed killer. This research will simulate how water pollution affects different aquatic species and how that ultimately leads to environmental changes, while evaluating the most effective methods to conduct this research.
-

The Efficacy of Physical Therapy for Pain Management in Women with Endometriosis: A Systematic Review
Courtney Portaro, Kiley Morrison, Samantha Miller, Sabrina Di Tucci, and Amy Tremback-Ball
Abstract
Background: Endometriosis is a disorder in which benign endometrial tissue grows due to atypical endometrial glands that form outside of the uterus. The disorder causes pain, excessive bleeding, dyspareunia, and may affect quality of life. Common medical treatment includes NSAIDS, hormonal therapy and surgery. Non-traditional interventions such as physical therapy may also be an option. The purpose of this review is to examine the effectiveness of physical therapy in decreasing pain and improving quality of life for women with endometriosis.
Methods: A review was performed August/September, 2020 using CINAHL Complete, PubMed, PEDro, and Academic Search Ultimate. Search terms included endometriosis, exercise, physical therapy, physiotherapy, and rehabilitation. Inclusion criteria were peer-reviewed randomized controlled trials, meta analyses, articles published in the last 15 years, and full text English. A hand search was also conducted.
Results: 11 studies met the inclusion criteria. There were 2 level 1, 2 level 2, and 7 level 3 on the hierarchy of evidence scale included in the study. Articles were grouped into the following categories: modality therapy, physical activity, manual therapy, combined intervention and meta analysis.
Conclusion: Research has shown a positive relationship between the use of combined physical therapy interventions as means of pain management for women with endometriosis. The study is inconclusive regarding use of a single intervention. The role of physical therapy for treating endometriosis needs further research to determine the best protocol for endometrial pain management.
-

The Opioid Epidemic and Nursing: How Can We Help?
Julia Randazzo
Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) is a problematic pattern of opioid use that causes significant impairment within a user's daily life. The opioid epidemic has led to excessive financial burdens on federal state and local governments; private health insurance; and society at large. This poster will discuss if there is a way to combat the opioid epidemic as a healthcare system and how nurses can help.
-

The Effectiveness of Aquatic Therapy, Robot Assisted Gait Training, and Virtual Reality on Patients with Parkinson's Disease: A Literature Review
Atasha Rehrig and Kristen Southard
Background & Purpose: Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects a person’s central nervous system (CNS) as well as dopamine production. Most cases of PD cause the patient to have postural instability, difficulty with ambulation, as well as a resting tremor. Patients diagnosed with PD show a slow decline in overall function and therefore, need to maintain physical activity in order to plateau PD. Traditionally, patients with PD undergo conventional methods of physical therapy (PT) to help plateau their disease. Our literature review looked into the effectiveness of non-traditional methods such as aquatic therapy, robot-assisted gait training (RAGT), and virtual reality (VR). Methods: We started our search in January 2021, using the PubMed database, and found 7,222 articles. Using the combination of “Parkinson’s disease” with the terms “aquatic therapy”, “robot-assisted gait training”, “virtual reality”, “pathophysiology”, “end-effector”, and “stepping time” and narrowed down our articles to 11. As this is a literature review, we would skim the abstracts and then decide from there whether to read the entire article to use it for our research. Results & Discussion: Aquatic therapy, RAGT, and VR are all beneficial to individuals with PD when looking for balance improvement. Conclusion: More research is needed in aquatic therapy, RAGT, and VR when looking into the effectiveness and benefits for individuals with PD and PT should consider treating patients with PD with non-conventional methods if available.
-

Nurse Residency Programs: Are They Beneficial?
Nadiyah A. Rivera
New graduate nurses often feel unprepared for professional practice. Nurse Residency Programs were developed in order to prepare graduate nurses for professional practice within the hospital. Nurse residency programs prepare new graduate nursing students by enhancing their critical thinking skills and role satisfaction before transitioning to professional nursing practice. Establishment of nurse residency programs leads to more competent nurses and better patient care. These programs increase critical thinking skills, competence, and preparedness, which leads to higher retention rates. Nurse residency programs demonstrated that there is a smoother transition from graduate nurse to registered nurse and improves both quality and safety of care, as well as retention rates for new nurses.
-

The Effects of Hippotherapy on Postural Control in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review
Anamarie Rogers and Paisha Glisson
The Effects of Hippotherapy on Postural Control in Children with Cerebral Palsy
Study Design: Systematic Review
Purpose: The purpose of this systematic review is to summarize and evaluate the most recently published research focusing on the effects of hippotherapy on postural control in children with cerebral palsy.
Methods and Measures: Two searches of literature were performed, the first in August 2020 and January 2021, using PubMed, Academic Search Ultimate and ScienceDirect databases. Peer reviewed hippotherapy and hippotherapy simulator studies for children aged 2-25 with cerebral palsy that examined postural control were included. Articles published prior to 2010 as well as articles based on therapeutic horseback riding were excluded. The PEDro scale was used to evaluate the quality of evidence.
Results: One hundred and seventy two articles were obtained; thirteen articles met all inclusion criteria and were included in this review. Quality of evidence was good, as the average PEDro score of the selected articles was 6.07. The change of postural control was then examined.
Conclusion: A review of the current literature indicates that hippotherapy is beneficial for patients with cerebral palsy. Evidence suggests that hippotherapy can significantly improve postural control and directly influences gait, dynamic balance, functional performance, trunk stability and quality of life. Although the current volume of evidence is limited, the published results clearly demonstrate that hippotherapy has a positive impact on the postural control of children with cerebral palsy.
-

The Reformation of Public Memory: Campaign for Redress Shifts Public Memory of Comfort Women Issue
Sara Shields
The comfort station system established by the Japanese during World War II institutionalized sexual violence against women in order to supposedly prevent both violent rapes and the spread of sexually transmitted diseases among Japanese soldiers. There are still arguments and denial over the issue of comfort women today, stating that these women were there of their own free will and were not enslaved. Until recently, they were regarded as “military prostitutes,” and were viewed as a disgrace by their respective cultures. However, evidence gathered since the early 1990s indicates that not only were comfort women sexual slaves of the Imperial Japanese military, but that the Japanese government and military directly collaborated to establish the comfort station system and to procure the women for them. A campaign to secure redress for the survivors began in 1992 and has been successful in reshaping public memory around the comfort station system.
-
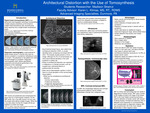
Architectural Distortion with the Use of Tomosynthesis
Madison Skwirut
Abstract
Architectural distortion on digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) can occur due to benign and malignant causes. DBT is a mammographic technique that incorporates multiple angular projections of the breast to enable three-dimensional reconstruction while only compressing the breast once. DBT creates a better detection of distortion compared to a 2D mammography. Architectural distortion is found when the two breasts are compared and one breast has an abnormal tissue pattern. When examining the two breast with each other they should mirror one another, so when there is architectural distortion there could be contour abnormalities, trabecular thickening, and trabecular disorganization. When architectural distortion becomes questionable on diagnostic imaging, MRI may be performed. Along with MRI, ultrasound is another tool used to help in the final diagnosis of benign or malignant. Malignant cases are more noted in 6.8%-50.7% of the cases due to ductal carcinoma. Architectural distortion on DBT is less likely to represent malignancy if there is no sonographic correlate. Few studies have focused on tomosynthesis detected architectural distortions to date, and optimal management of these distortions have yet to be distinct.
Keywords: architectural distortion, digital breast tomosynthesis, malignant, MRI, ultrasound, breast
-

Nursing: Global Impact Increases Healthcare Effectiveness
Madison Slacktish
The discipline of nursing has a major impact on the world globally. Research has found when nurses collaborate across boarders, then patient outcomes tend to increase. Disease does not stop because there is a boarder from one country to the next. Therefore, worldly collaboration has positive influences on how nurse's practice and ways to change protocols to increase better patient outcomes.
-

A Study of Bone Histology Procedures and Applications
Breanna Smith
Bone histology paired with ontogeny can allow for discovery of the way in which an individual grows. “Bone” umbrellas so many types and patterns which are all linked to both environmental and genetic influences. Vascular patterns allow for the differentiation of growth rates and growth periods. Veracious usage of terminology and proper specimen selection can lead to these explanations.
-

Respiratory Gating in Radiation Therapy Without Adequate Breath-Holds
Ethan Snyder
Respiratory gating is used in radiation therapy to maximize the effect of radiation on the target area while also minimizing radiation exposure to surrounding normal tissue. This is accomplished through the use of breath-holds during treatment. This study focuses on a specific patient who had difficulty holding their breath for the required treatment time. The question being asked was, would inadequate breath-holds lead to a negative effect on the patient’s outcome? This study was conducted by following the patient’s treatment course and comparing end results with similar patients who were able to complete breath-holds to a more satisfying degree. The result of the study was that the patient having inadequate breath-holds did not negatively affect the patient’s end outcomes in a significant manner. The conclusion to this being that the respiratory gating system that was employed was able to rectify any negative effects stemming from inadequate breath-holds. A possible implication from this study could be that more patients are eligible for respiratory gating techniques than previously thought due to the effectiveness of gating systems in compensating for poor breath-holds.








