Student Research Poster Presentations showcase innovative research by Misericordia students across all disciplines.
-

Efficacy of Exercise Interventions Applied to Populations Diagnosed with Anorexia Nervosa, Bulimia Nervosa, and/or Binge Eating Disorder(s) on Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review
Lauren Anderson, Patrick Hoffman, Jared Houser, Marissa Prince, and Kaitlyn Weatherby
Efficacy of Exercise Interventions Applied to Populations Diagnosed With Anorexia Nervosa, Bulimia Nervosa, and/or Binge Eating Disorder(s) on Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review.
Lauren Anderson, SPT; Patrick Hoffman, SPT; Jared Houser, SPT; Marissa Prince, SPT; Kaitlyn Weatherby, SPT; Kristen Karnish, PT, MPH, D.Ed
Objectives: Investigate the impact of resistance training, yoga, and aerobic exercise on perceived quality of life and physiological function for individuals with eating disorders.
Data Sources: EBSCO-PsycINFO, EBSCO-Health Source, PubMed, and CINAHL were searched in September 2021 and January 2022. Indexing terms used for article retrieval included the combination of: physical therapy, physiotherapy, rehabilitation, eating disorder, anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge eating, exercise, exercise interventions, resistance training, yoga, and aerobic exercise.
Study Selection: Eligible articles included English translation, peer-reviewed, publication date after 2009, subjects < 50 years old, interventions within physical therapy scope of practice including resistance training, yoga, or aerobic training, and PEDro score ≥ 3. Seventy articles were retrieved for evaluation. Studies were selected following consensus by multiple researchers. Eleven articles met inclusion criteria.
Data Extraction: Articles were analyzed for quality and validity using the PEDro scale and a hierarchy of evidence scale. Data extracted from each article included subject demographics, interventions provided, assessment tools, outcomes, limitations, and conclusions.
Data Synthesis: Researchers found that for all participants diagnosed with eating disorders, high intensity resistance training was more effective in improving and maintaining quality of life and functional strength measures as compared to low/moderate intensity exercise. Experimental groups who performed yoga or received cognitive behavioral therapy with resistance interval training demonstrated increased psychological well-being and emotional regulation. Exercise had a positive effect on BMI and frequency of binge-eating behaviors in individuals with binge eating disorder. Physiological measures were also improved in subjects who engaged in physical activity alongside counseling with a mental health physical therapist.
Conclusion: Inclusion of exercise for individuals receiving treatment for eating disorders can positively affect perceived quality of life, body composition, and physiological function. Future research is recommended to explore the role of physical therapy in eating disorder treatment including investigation of long-term effects and treatment along the continuum of recovery.
Disclosures: No conflicts of interest present.
Key Words: physical therapy, eating disorder, resistance training, yoga, aerobic exercise, quality of life
-

Need for Comprehension Remediation in a University-Based Online Reading Clinic
Patricia Ash
The significant areas of concern for this research include determining the most effective comprehension strategies that will address the needs of students who struggle with comprehension. There is no doubt that technology and alternative means of instruction have to be explored and used for education; however, the platforms must be evaluated with specific criteria to allow for seamless instruction and student interaction. Finally, this research will evaluate if the need for a reading clinic is one that school districts think needs to be filled.
-

Vestibular Rehabilitation as an Early Intervention in Athletes Who Are Post-Concussion: A Systematic Review
Gabrielle Babula, Edward Warunek, Grace Nikolski, and Katherine Cure
Background: Sports-related concussions (SRC) are a common injury sustained by many athletes of all different age groups and sports. The current standard treatment is rest followed by aerobic activity. Little has been researched on the effects of vestibular rehabilitation for concussion treatment, especially in physical therapy practice.
Objective: The purpose of this systematic review was to research the effects of early intervention of vestibular rehabilitation and an athlete’s time to return to play compared to rest alone.
Methods: Two searches were conducted (August 2021 & January 2022). Databases looked at were CINAHL complete, MEDLINE, PubMed, Wiley online database, and one hand search. Search terms included vestibular rehabilitation or vestibular therapy, concussion, or mild traumatic brain injury or mild TBI, athletes, sports, athletics or performance, and early interventions or therapy or treatment.
Results: Yielded 11 articles (randomized control trials and retrospective cohort studies). Inclusion criteria were athletes who sustained a SRC, incorporation of vestibular rehabilitation in athletes recovery, and early vestibular intervention tools.
Discussion: Incorporating visual interventions and cervical manual therapy into early rehabilitation significantly reduces symptoms and time to return to sport. However, balance interventions do not have a significant effect on reducing time to return to sport when used as a sole intervention.
Conclusion: Beginning VRT as early as 10 to 30 days post-concussion has been shown to contribute to a quicker resolution of symptoms and a quicker return to sport. However, more data collection needs to be performed to determine the effectiveness of early intervention in concussion recovery.
-
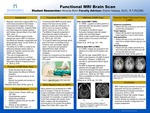
Functional MRI Brain Scan
Miranda Bohn
This project explains a functional MRI (fMRI) brain scan and the role magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can play in helping patients receive diagnoses and prepare for surgery. The purpose, contraindications, outcomes, methods, and common task performed are also discussed. A functional MRI records different areas of the brain that are active when the patient performs different tasks. Some of the different tasks that are done during task-based fMRI are sentence completion, finger tapping, verb generation and word generation. There are also times during the scan when the patient just lays still known as a resting-state fMRI. This brain scan has the potential to guide the planning for surgery, help assess the effects of different disorders, explain brain anatomy, and monitor tumor growth and function. fMRI brain scans are continuing to produce high-quality images that will help discover future behaviors and disease processes. Therefore, further studies are needed for improved outcomes for diagnosis and surgical preparation for patients.
-

Treatment of Brain Metastases Using Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Mikayla Cavenas
This project explains the effectiveness of stereotactic radiosurgery compared to whole-brain radiation therapy in managing cognitive function and improving the quality of life in patients diagnosed with brain metastases. Metastatic brain cancer is caused when cancer spreads to the brain from other areas of the body. The cancerous cells will break away from their original location and travel through the bloodstream or lymph system. Stereotactic radiosurgery is the administration of high-dose radiation that is delivered in a single or up to five sessions to a specific brain tumor under the guidance of real-time imaging. SRS patients allow for a similar survival rate, but a generally better cognitive function compared to WBRT patients. A setback of SRS treatments is the risk of missing remnants of minuscule tumors leading to tumor regrowth. Brain metastases can be treated on three different types of machines such as a linear accelerator, gamma knife, or proton beam therapy. A case study involving a 56-year-old woman who was originally diagnosed with carcinoma of the left breast in 2009, which later metastasized into her lungs in 2020 was cured of both cancers. In late 2020, and early 2021 cancer metastasized into her brain where her doctor suggested stereotactic radiosurgery. With further research on SRS treatment, it can only advance patient outcomes and treatment options for the future.
-

Effect of Core Stabilization Training for Improved Running Performance, Efficiency, & Risk of Injury in Young Novice Athletes: A Systematic Review
Melissa Cencetti, Sarah Reeder, Ashleigh O'Malley, Levi Roberts, Trent Woolcock, Ryan Romaine, and Garrett Murray
Abstract:
Background: For years there has been a debate on the importance of proper running mechanics & its effect on athletic performance and injury prevention. Many argue that running is a natural motion, & athletes will instinctively adopt the most efficient running form. However, research suggests that since running is a complex full body movement, technique can affect performance and the occurrence of injury. Muscle activity imbalances & altered activation patterns are associated with potential injuries and decreased running economy, which is explored further in this review. The purpose of this systematic review is to examine the effects of core stabilization & strengthening exercises on running dynamics in novice athletes (12-25). The role of core stabilization in potential injury prevention strategies is also explored.
Methods: A literature search was completed in September 2021 and January 2022 using PubMed and CINAHL Complete. Articles included in the systematic review were analyzed for quality based on the PEDro scale & level of evidence scale.
Results: Nine articles were chosen based on the following criteria: publication 2011 - present, novice athletes (12-25), & articles that examined the relationship between core stabilization and running dynamics or risk of injury in athletes. Three additional articles were identified through a hand search. All articles were experimental, & had an average score of 5.58/10 on the PEDro scale, & ranged from Level II- Level IV on a hierarchy of evidence scale.
Conclusion: To date, the current literature on the effect of core strength or core stabilization for running performance & injury prevention has been inconclusive. No firm conclusions can be drawn on the effectiveness of core stabilization/strengthening on running performance or injury prevention. This review identifies the need for continued research in the realm of core stabilization, core strength training, and its relationship with running performance and injury prevention.
-

Co-Teaching in High School
Ashley Evans
Students with and without disabilities are entitled to a free and appropriate public education. All students should be given the best education no matter the circumstances that may be present. Implementing the co-teaching model and framework into high school general education classrooms can benefit all students. Where there are benefits with teaching models, there are also drawbacks that can cause the implementation of the model not to be implemented as created. Difference causes can cause this that school districts may or may not be able to control. The lack of professional development, certifications of the educators, and defining the roles and responsibilities that each educator will hold in the classroom are just a few of the drawbacks that can cause co-teaching not to be implemented to the best of the ability in which it was created.
-
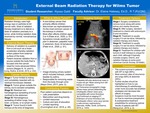
External Beam Radiation Therapy for Wilms Tumor
Alyssa Galdi
This project explains Wilms tumor cancer and the role radiation therapy can play in treating patients who have the disease. General statistics, symptoms, cancer severity, contributing factors, imaging options, and treatment options are also discussed. Wilms tumor is a type of childhood cancer that starts in the kidneys. It is the most common type of kidney cancer in children. About 9 of 10 kidney cancers in children are Wilms tumors. Treatment for Wilms' tumor involves surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. The type of radiation therapy used for Wilms tumor is external beam radiation therapy. There are five stages of Wilms tumor cancer and treatments vary by their stage. Poor patient outcomes depend on contributing factors such as late presentation, malnutrition and drug toxicity, limited resources, culture and lack of education, and limited reporting. In saying so, surgeons need to know how to maximize preoperative and postoperative treatment possibilities for achieving optimal results of patients with Wilms tumor in the future.
-

The Effects of Neuronal Growth Factors on LPS-Activated Schwann Cells
Caitlyn E. Henry, Peyton Kimmel, and Angela Asirvatham Ph.D.
Schwann cells (SCs) are the principal support cells of neurons in the peripheral nervous system, that both myelinate axons for the rapid conduction of electrical impulses as well as assist in axonal repair during nerve injury. During nerve injury, SCs secrete tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)1,5,6 and other proinflammatory mediators1,6, attracting macrophages to the site of injury to induce inflammation and clear myelin debris.1,6 Once the debris is cleared, the neuron stimulates SC proliferation by secreting neuronal mitogens, such as heregulin3,4, and an unknown factor that activates the cAMP pathway3, an important regulator of cell division.3,4 In vitro, SCs can be treated with an artificial plant extract called forskolin3,4 to activate the cAMP pathway. Studies show that heregulin and forskolin act synergistically to enhance SC proliferation under normal, non-inflammatory conditions.4 Although the role of cAMP in proliferation and axonal regeneration is well-known, not much has been explored about its function in SCs during nerve injury and inflammation. In vitro, inflammatory conditions can be simulated by treating SCs with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a cell-wall immunostimulatory component of Gram-negative bacteria.1,2,6 In most mammalian cells, LPS binds to a transmembrane protein called toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)1,2,6, activating both the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway1,2,6 and the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway2,6, to promote the secretion of inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α.1,2,6 With that being said, the aim of this preliminary study was to determine the role of the cAMP pathway in SCs during LPS-induced inflammation. It was hypothesized that SCs stimulated with LPS and growth factors will have higher proliferation than SCs treated with LPS only.
-
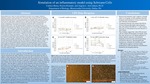
Simulation of an Inflammatory Model Using Schwann Cells
Caitlyn Henry, Peyton Kimmel, and Angela Asirvatham
During peripheral nerve injury, the myelin surrounding the neuronal axons is damaged, initiating an inflammatory response to remove myelin debris. Once myelin debris is cleared, Schwann cells acquire a proliferating phenotype which allows them to grow and divide so that remyelination can occur. The neuron stimulates Schwann cell division by secreting growth factors, like heregulin, and an unknown growth factor that activates the cAMP pathway. Although the role of cAMP in axonal regeneration is well-known, not much has been explored about its function in Schwann cells during nerve injury and inflammation. To simulate an inflammatory environment, the S16 Schwann cell line (SC-2941) was activated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a cell-wall immunostimulatory component of Gram-negative bacteria. It was hypothesized that Schwann cells stimulated with LPS and growth factors will have higher proliferation in comparison to LPS treatment only. Schwann cells were treated for 1, 3, 12 or 24 hours with no growth factors (control media, N2), 12.5 ng/mL heregulin (H), 2mM forskolin (F) or H+F and various doses of LPS at 5, 50 or 500 ng/mL. Using the MTT proliferation assay, preliminary studies in 24-hour cultures reveal that cell proliferation, as measured by optical density, was significantly higher in cells treated with 5 ng/mL of LPS+F (0.846 ± 0.054), and H+F (1.023 ± 0.189) in comparison to cells grown with H (0.699 ± 0.057) or N2 only (0.765 ± 0.016). In contrast, cells treated for 1, 3 and 12 hours, with various concentrations of LPS revealed an overall decrease in proliferation when compared to 24-hour cultures. However, cultures treated with LPS and F or H+F, for all time points, showed an increase in cell growth when compared to N2 and H. In summary, it appears as though a combination of LPS and forskolin, with or without heregulin, may promote more Schwann cell proliferation than LPS alone. These findings also suggest that, when LPS-activated cells are treated with heregulin or forskolin, alone, they may activate two very distinct pathways to initiate opposite responses, with heregulin hindering cell division and forskolin promoting cell division. However, when heregulin and forskolin are combined, the forskolin-activated cAMP pathway appears to promote higher proliferation to offset the decrease in proliferation initiated by the heregulin pathway. Considering these results, it appears that the cAMP pathway in Schwann cells may play a major role in the inflammatory environment during nerve injury.
-

Academic Integrity in Health Science Education
Camille Hondromaras and Nicole Macko
Academic misconduct in the United States has been on the rise and there are a variety of factors playing into the reason. Academic misconduct has persisted in postsecondary education, with rates of serious cheating in the United States increasing from 75% to 82% among students, over a thirty-year time frame (Medina). The present research was conducted to evaluate the prevalence of academic misconduct, the variety of modes used to break academic integrity, the rationale behind it per individual, and how these answers could influence future careers. A study was conducted with 39 participants ranging from high school sophomores to master's degree students with questions posed that could give insight to how and why academic integrity is becoming a fixture of the past. The results of the study showed that of the total participants, 48% admitted to academic misconduct with modes of cheating including cellular devices, student peers, notes, and online services. Concerns exist that engagement in academic dishonesty by health science students may transfer to professional misconduct in the clinical setting, thereby jeopardizing the quality of patient care (Bloomfield).
-

Clinical Indication Appropriateness of Bilateral Lower Extremity Venous Exams
Kristina Horan and Breana Doyle
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the appropriateness of bilateral lower extremity venous exam orders. The study encompassed final reports of 216 bilateral lower extremity venous exams that took place in December 2021 from three separate medical facilities. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Appropriate Use Guidelines for Non-Invasive Vascular Studies were used to determine if the exams were ordered appropriately. The results were 159 duplex exams were ordered appropriately and 57 were not appropriate. The findings concluded that a majority of the bilateral lower extremity venous exams were ordered appropriately.
-

The Effect of Creatine on Immortalized Schwann Cell Proliferation
Peyton Kimmel, Caitlyn Henry, and Angela Asirvatham
Creatine is an important component of the high-energy phosphate transfer to regulate cellular levels of ATP. The functions of creatine supplementation are well studied in the muscular and skeletal system, however the impact of creatine in the nervous system, specifically Schwann cells, is relatively unknown. Schwann cell growth in vitro is facilitated by heregulin, a neuron secreted growth factor, and forskolin, a pharmacological agent that activates cAMP. In peripheral nervous system injuries, recovery time is based around Schwann cell’s ability to proliferate and differentiate, and it is unknown what role creatine plays in this process. It was hypothesized that increasing creatine concentrations in combination with growth factors would augment Schwann cell growth. Immortalized Schwann cell line S16 cells were treated with N2 (control), heregulin (12.5ng/mL), forskolin (2µM) and heregulin plus forskolin for 24 hours. To determine the optimal dose of creatine for the Schwann cells, doses of 200nM creatine, 2µM creatine, and 20µM creatine were added to each of the previously stated treatments, and was repeated for 1-, 6-, and 12-hour timepoints. At the 1- and 6-hour time points 200nM and 2µM showed the greatest proliferation amongst the three doses and, the cells were most influenced by the presence of heregulin (108.9±5.45), (113.3±20.1). A synergistic effect was noted between heregulin and forskolin at both time points (104.86±2.9), (107.76±20.88). At the 12- and 24-hour time points the optimal creatine dosage for proliferation was 2µM and, the cells were most influenced by the presence of forskolin (108.38±7.6), (110.52±1.60). These time points showed a synergistic effect as well. This suggests that at shorter timepoints, creatine stimulates a different pathway than at longer timepoints. In summary, these findings suggest that creatine stimulate proliferation through different pathways depending on concentration and timepoint.
-

CT-Guided Bone Biopsy
Meredith Lambertino
Abstract
Bone biopsies are used to diagnose cancer that may have spread to the bone or is already in the bone. For accurate cancer diagnoses, interventional radiology (IR) bone biopsies are best done under the guidance of computed tomography (CT) imaging. The equipment required for CT during this procedure includes a gantry, table, and operator console. IR supplies all the needles, sterile drapes, and CT Localization grid. Bone biopsies require the use of a variety of needles to plan the procedure and collect a cell sample for analysis. The benefits of this procedure include a brief recovery, a less invasive procedure, and only requires the use of a local anesthetic. The risk of infection associated with CT-guided bone biopsies occurs less than one in a thousand. Compared to blind bone biopsies, CT-guided biopsies provide an accurate diagnosis about ninety percent of the time. Blind bone biopsies are unable to account for anatomical differences between patients. Studies found that CT-guided biopsies are better for inserting the needle in the correct spot because CT allows for visualization of the field.
-
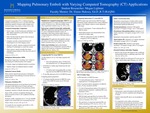
Mapping Pulmonary Emboli with Varying Computed Tomography (CT) Applications
Megan Lightner
This project explains different computed tomography (CT) applications that aid in the detection of pulmonary emboli. Pulmonary emboli are blood-clots that form elsewhere in the body and travel to the heart and lungs, increasing the risk of blocked arteries. CT has become the primary tool in detecting pulmonary emboli and offers different applications to which iodine map technology can be applied. These applications include multidetector computed tomography (MDCT), dual-energy computed tomography angiography (DECTA), and subtraction CT. Iodine maps detect irregular blood flow induced by pulmonary emboli. Comparisons between iodine maps derived from the different CT applications are discussed. Iodine concentration measurements are also discussed to describe differences in blood flow within normal, partially occluded, and completely occluded parenchyma. Potential problems with iodine maps are also included to demonstrate how the benefit must outweigh the risk when utilizing the iodine maps. The incidence and mortality rate of pulmonary emboli are increasing, which emphasizes the urgency for detection and treatment. With the use of iodine maps, pulmonary emboli may be accurately diagnosed more often and lead to a decrease in mortality rates.
-

An Overview of Literature Related to Post COVID-19 Rehabilitation
Michael McGee, Zachary Davis, Mikayla Klimas, and Sierra Schertler
Objective: To complete a systematic search of available research on the role of physical therapy (PT) with managing post COVID-19 related conditions and common symptomatology in adults in the outpatient PT setting.
Data Sources: PubMed, CINAHL, Medline, Cochrane, Hand Searches
Study Selection: Searches were conducted to examine current data related to PT interventions and their effectiveness for treating post COVID-19 conditions in outpatient clinics. Articles were examined by researchers and evaluated for relevance based on the following criteria: articles in English, original peer reviewed articles, adult population (over 18), relevant PT interventions for rehabilitation, post-acute infection of COVID-19.
Data Extraction: Articles were reviewed and analyzed for relevance to implications regarding post-COVID-19 and potential PT rehabilitation interventions. Interventions were assessed in feasibility and applicability to an outpatient clinic setting. Articles were examined for content regarding the latest updates on disease criteria, manifestations, new classifications, and cohorts emerging as the pandemic progresses.
Data Synthesis: After article analysis, the findings include a key theme that PT services helped improve overall functional mobility and symptom management in patients after an infection of COVID-19. A combination of pulmonary rehabilitation, strength and aerobic training, and interval training have been shown to improve quality of life and manage residual symptoms of COVID-19.
Conclusion: PT has a growing role in the management of post COVID-19 deficits as well as implications related to long covid sequelae. By choosing the appropriate parameters and using available knowledge with current research, practitioners can improve patients’ functional mobility by helping resolve current conditions such as shortness of breath and fatigue. The focus of future studies should include more specific interventions and parameters related to managing the condition and finding the most effective treatment strategies.
-

Improving Classroom Climate and Engagement at the Secondary Special Education Level through the Implementation of Classroom Management Strategies
Pauline Mickavicz
A lack of professional development, the complexity of interventions, and limited data to reflect upon have implemented successful classroom management strategies challenging for special educators. These barriers negatively impact classroom climate and achievement in special education rooms. Educators should receive support to execute classroom management strategies confidently to decrease problem behavior and increase student engagement. Best practice classroom management strategies should be narrowed down to hone in on interventions and simplify the complexity of the delivery. Data collection will play an integral role in the reflection process and provide insight into how classroom management can be examined at the high school level.









